The Disease
Economic losses related to ileitis
Economic impact results mostly from productivity losses caused by the disease
Discover the causes here
HIGHLIGHTS
Based on a survey of swine veterinarians, the value of productivity losses and increased animal health costs in pigs affected by ileitis in the finishing phase was estimated to be USD4.65 per marketed pig.Based on results from case-control and experimental challenge studies, the value of productivity losses caused by ileitis in the finishing phase ranged from USD5.98 to USD17.34 per marketed pig.The cost of the variation in growth caused by ileitis makes it more difficult to feed and market pigs, this adding to the cost of the disease.The money spent on animal health interventions, such as vaccines, antimicrobials, veterinary services and diagnostics must be weighed against the benefit of reducing the productivity losses caused by ileitis.
History and Etiology of ileitis
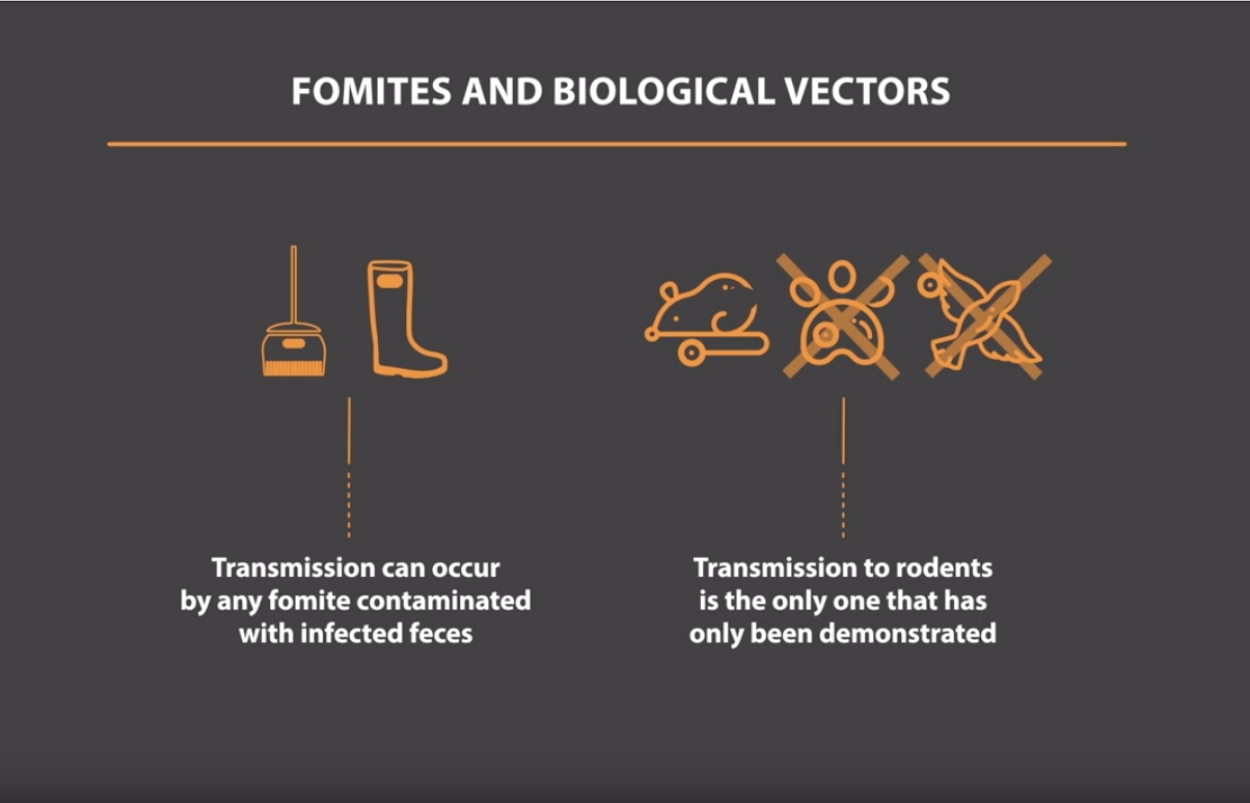
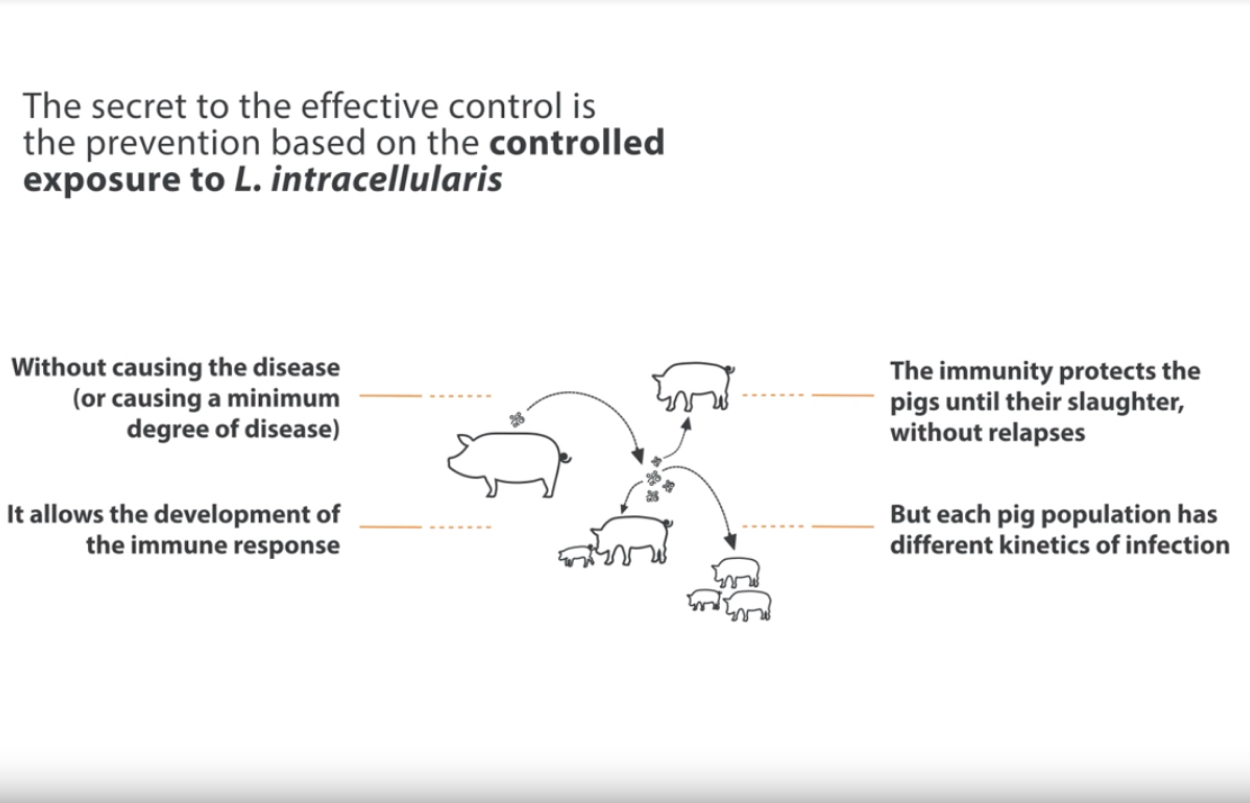
Epidemiology of ileitis

Pathogenesis of L. Intracellularis
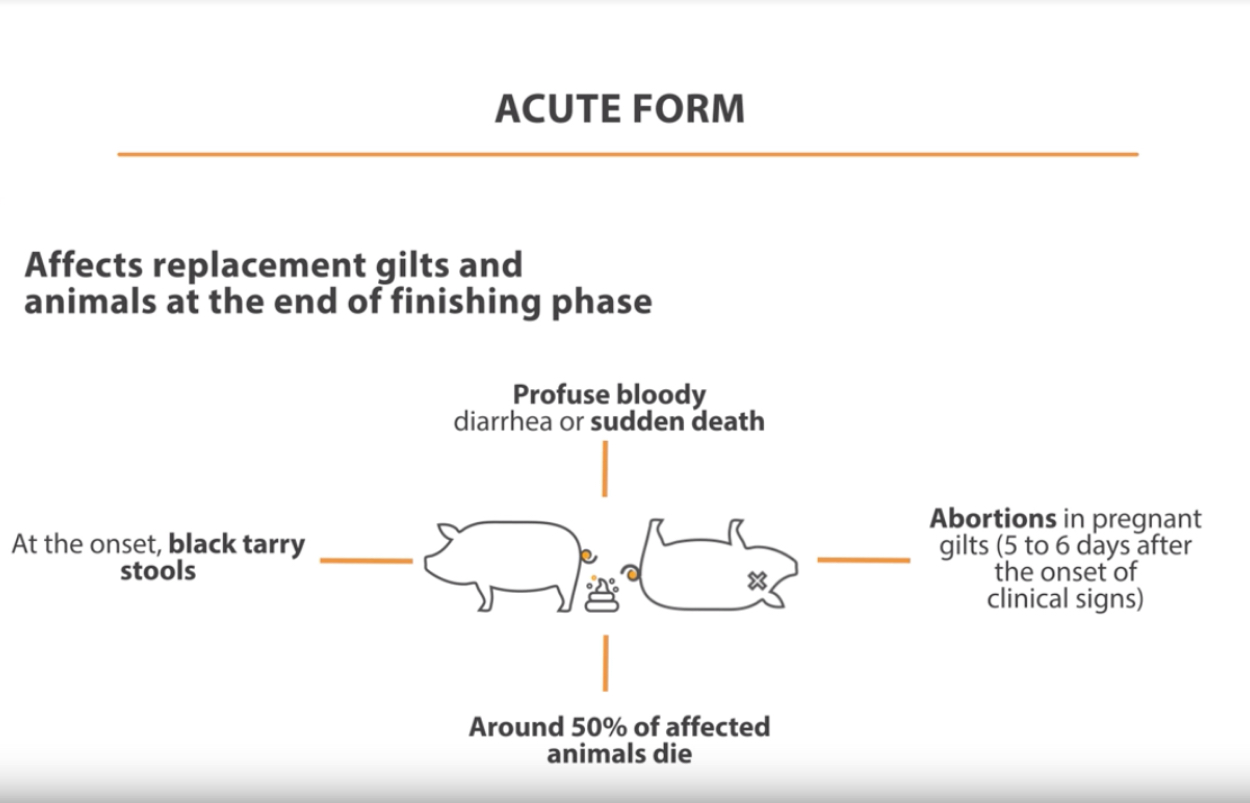
Clinical signs and forms of ileitis

Diagnosis of ileitis
Treatment of ileitis
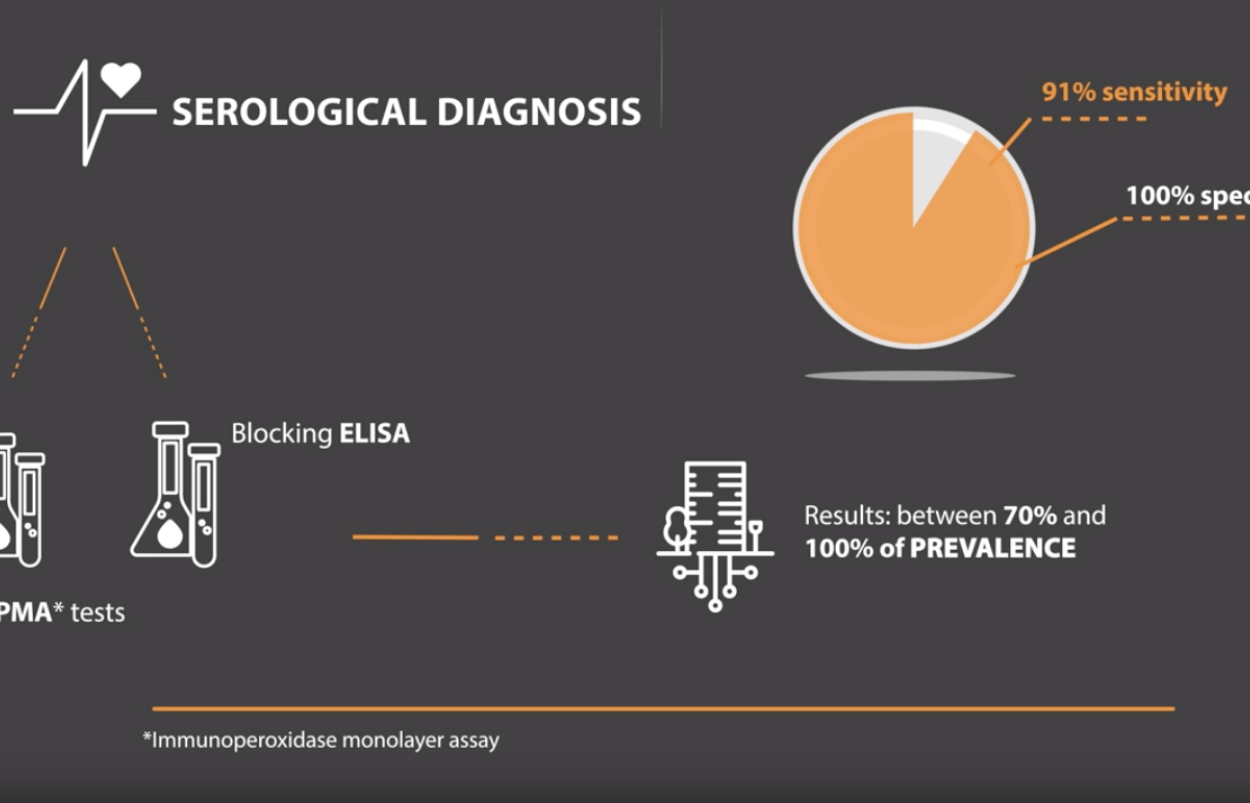
Prevalence of ileitis